Recent Advances of Wind-Solar Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems for Power Generation: A Review
Authors: Pranoy Roy; JiangBiao He; Tiefu Zhao; Yash Veer Singh
Extended Abstract:
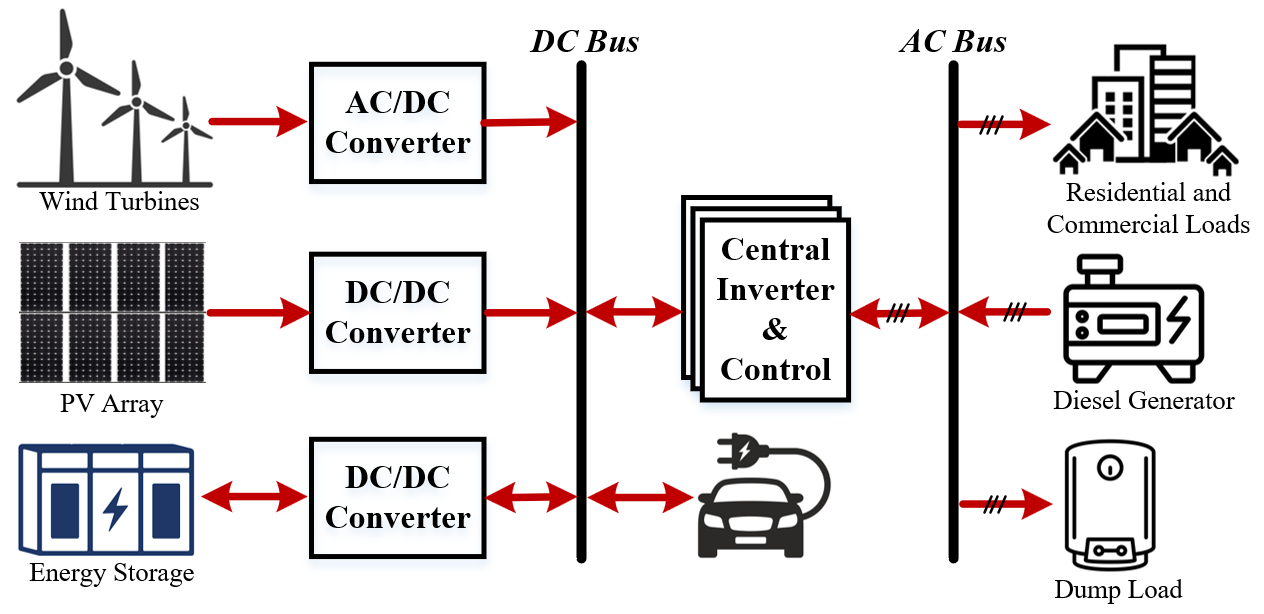
A hybrid renewable energy system (HRES) generally consists of two or more renewable energy sources with complementary power generation profiles, such as wind turbines and photovoltaic systems, along with a low-capacity energy storage system to provide non-intermittent power with increased system efficiency and improved stability. The objective of this study is to present a comprehensive review of various wind-solar HRES from the perspectives of power architectures, mathematical modeling, power electronic converter topologies, and design optimization algorithms. Since the intermittency of HRES can be further reduced by including an energy storage system, this paper critically reviews different types of hybrid energy storage systems, focusing on their coupling technologies and highlighting their major advantages and disadvantages. The basic mathematical modeling of photovoltaic and wind turbine power generation systems, as well as the degradation model of batteries and supercapacitors are also reported. Various HRES power converters and control strategies from the state-of-the-art have been discussed. Different types of energy source combinations, modeling, power converter architectures, sizing, and optimization techniques used in the existing HRES are reviewed in this work, which intends to serve as a comprehensive reference for researchers, engineers, and policymakers in this field. This article also discusses the technical challenges associated with HRES as well as the research scope for future advancements. Although considerable accomplishments have been achieved over the past decade on various HRES, such a comprehensive review helps to identify and fulfill the technical gaps to improve the efficiency, stability, and reduce the cost of the power grids.