Recent updates

Multichannel Asynchronous Triggering-Based Adaptive Output Feedback Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems with Actuator Faults
Authors: Xinpeng Fang, Huijin Fan, Lei Liu, Bo Wang Extended abstract: For a control system, the control commands need to be executed accurately by the actuator. However, harsh environments and aging hardware may cause actuator faults. As a consequence, the designed control commands cannot be executed correctly, and the control performance may be degraded. Meanwhile, in practical systems, signals are usually transmitted among different components through networks with limited bandwidth. Therefore, tolerating actuator faults while reducing resource consumption can significantly contribute to the safety enhancement and lifespan extension of the system. This paper proposes an adaptive event-triggered output feedback fault-tolerant control scheme for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown actuator faults. Multiple channels, including the state estimation filter-to-controller (S-C) channel, the parameter estimator-to-controller (P-C) channel and the controller-to-actuator (C-A) channel, are all event-triggered. Moreover, by designing a series of uncorrelated triggering conditions, the triggering of different channels is independent and asynchronous. The advantages of the proposed triggering mechanism are to 1) reduce the communication burden for multiple types of channels by decreasing the signal transmission frequency, and 2) reduce the computation burden by removing real-time integration. Therefore, the communication and computation burden of the system can be released ...
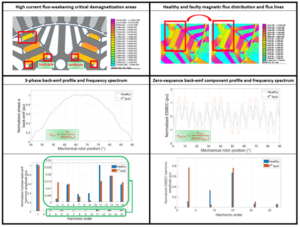
Local demagnetization fault detection in PMASynRM based on finite element modeling and characterisation
Authors: Jérémy Creux, Najla Haje Obeid, Thierry Boileau, Farid Meibody-Tabar Extended abstract: Good overall performances and efficiency of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines (PMSMs) are highly impacted by irreversible demagnetization faults. This paper proposes to analyze the electromagnetic behavior of a faulty Permanent Magnet Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor (PMASynRM) with neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) rare-earth magnets, to identify frequency fault signatures and develop an efficient fault indicator. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is used to determine high current flux-weakening critical demagnetization areas in the rotor, to model local demagnetization defects and to evaluate precisely post-demagnetization characteristics of the baseline machine. The study focuses on flux and back-emf time and frequency analysis for their high potential to identify low severity fault signatures. The results mainly show that magnetic flux density distribution is impacted, and flux lines are disturbed and reduced in the demagnetization area. Also, the 3-phase back-emf is distorted with a third-order harmonic amplitude increase, while ninth and eleventh-order harmonics amplitude are significantly trended downwards. Finally, the Zero-Sequence Back-Emf Component (ZSBEC) frequency spectrum is significantly impacted, especially harmonics multiple of 3. Therefore, we suggest using this frequency pattern to develop a fault detection index which allows quantifying, with high sensitivity, the severity of local ...
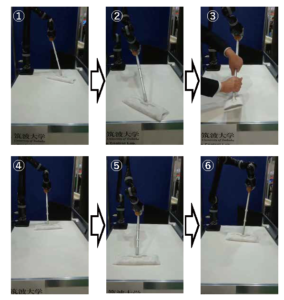
Bilateral Control-Based Imitation Learning for Velocity-Controlled Robot
Author: Sho Sakaino Extended abstract: Machine learning is now playing important role in robotic object manipulation. In addition, force control is necessary for manipulating various objects to achieve robustness against perturbations of configurations and stiffness. The author's group revealed that fast and dynamic object manipulation with force control can be obtained by bilateral control-based imitation learning. In this method, operators' skills including force control can be imitated by using neural networks. However, the method is applicable only in robots that can control torque, while it is not applicable in robots that can only follow position or velocity commands like many commercially available robots. Then, in this research, a way to implement bilateral control-based imitation learning to velocity-controlled robots is proposed. In the proposed method, torque references of bilateral control-based imitation learning are transformed into velocity commands by using an admittance control-like procedure. The validity of the proposed method is experimentally verified by a mopping task, and a robot could continue to operate even if the length of a mop was suddenly changed. 2022 Best IEEE Industrial Electronics Society Conference Paper Award (paper presented at 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (ISIE) Check full paper at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9576326 ...
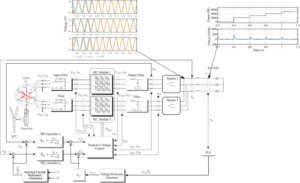
Active and Reactive Power Control based on Predictive Voltage Control in a Six-Phase Generation System using Modular Matrix Converters
Authors: Sergio Toledo, Magno Ayala, Edgar Maqueda, Raul Gregor, Alfredo Renault, Marco Rivera, Tomislav Dragicevic and Patrick Wheeler Extended abstract: Renewable energy generation for distributed generation systems are emerging as a plausible solution for the world’s growing energy demands. In this context multi-phase wind generation systems are a feasible option, consisting of a renewable AC source that needs efficient and controlled power conversion stages. The possibility to split the power and the current between a higher number of phases, allowing per-phase inverter power rating reduction is the main reason of selecting multiphase topologies for wind turbines. In this paper a novel active and reactive power control strategy based on two cascade control loops using a combination of classical PR controller and Model Based Predictive Voltage Control is proposed. Furthermore, the generator is a permanent magnet synchronous machine, and the power stage is based on a multi-modular direct matrix converter (MMC) topology providing interesting features to the scheme such as the ability to provide three-phase sinusoidal voltages with variable amplitude and frequency using fully controlled bi-directional switches without the use of storage energies elements reducing the size and weight. These characteristics make it attractive to use the MMC in applications where ...
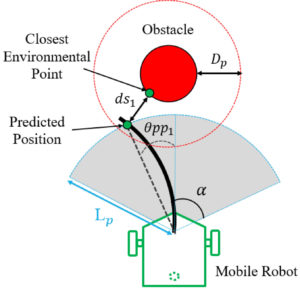
Remote Control Method With Force Assist Based on Time to Collision for Mobile Robot
Authors: Ryo Masaki, Naoki Motoi, Masato Kobayashi Abstract: This paper proposes a remote control method with the force assist to improve the operability of a mobile robot. The force feedback is generated on the basis of the time to collision (TTC) and translational velocity. The TTC is calculated from the predicted trajectory and environmental information, and is used as an indicator of the possibility of collision. If the possibility of collision is low, the force assist is not implemented. Therefore, the operator can control the mobile robot with a low manipulation force. On the contrary, if the collision possibility is high, the force assist is implemented. This force assist is classified on the bases of two cases according to the translational velocity. In the case of the low translational velocity, collision avoidance can be achieved via modification of the angular velocity alone. As a result, the proposed method generates a force assist for the angular velocity alone. On the contrary, if the translational velocity is high, it is necessary to modify both the translational and angular velocities to avoid collision. In this case, a force assist is generated for both velocities. Finally, the operability improvement resulting from the proposed method is confirmed experimentally. IEEE 2019 International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM) – ...
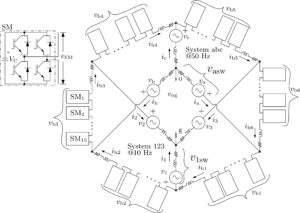
A comparative evaluation of modulation strategies for Hexverter-based Modular Multilevel Converters
Hector R. Robles-Campos, Fernando Mancilla-David Extended abstract: Within the last two decades modular multilevel converters topologies have received plenty of research attention given their possibilities to be used in medium and high power levels. The main advantages of multilevel converters against the very famous two-level power converter are: reduced requirements for series connection of semiconductor devices for the same voltage level, improved quality of the processed power, and relatively low switching frequency. On any modular multilevel topology, it is required to determine n number of submodules (SMs) to be inserted at any given time, so that, the process of transferring power from source to load, at minimum losses, can be achieved. In addition, a key objective is to be compliant with international standards, such as the IEEE 519 and the IEC 61000-3-2, regarding the quality of the power being supplied to the load. Different modulation techniques such as: nearest level control (NLC) and phase disposition-sinusoidal pulse width modulation (PD-SPWM,) have been already implemented for some multilevel topologies. Nonetheless, there is a lack of a detailed assessment regarding multilevel modulation strategies applied for the direct AC-AC modular multilevel topology "Hexverter'' that in turn is depicted in Fig. 1 Fig.1 Hexverter Topology ...
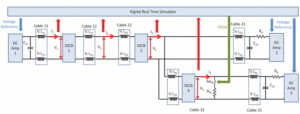
Testing Operation and Coordination of DC Solid State Circuit Breakers
Authors: James Langston; Andrew Rockhill; Karl Schoder; Michael Sloderbeck; Michael Steurer Extended Abstract: An approach for testing the operation and coordination of medium-voltage dc solid state circuit breakers (SSCB) for shipboard power systems is described. For the considered application, the rate of rise of current during a short-circuit is limited primarily by a small cable inductance. This high rate of rise, coupled with the need to interrupt the current prior to exceeding the limits of the power electronic switches in the SSCBs, necessitates a coordinated protection scheme which can isolate the fault within a matter of microseconds. Challenges in such tests include the high-voltage, high current, high rates of change of current, and the interconnection of devices within a system. Testing of the SSCBs in a system context presents a challenge, as the MVDC system to which these are to be applied has been realized neither in an actual shipboard implementation, nor in a land-based test site. In order to cope with these challenges and verify the operation of the SSCBs within a system context, a combination of tests and analyses are employed, including off-line simulation, controller hardware-in-the-loop simulation, hardware testing of a single SSCB, and coordination testing with multiple ...
Distributed k-means algorithm for sensor networks based on multi-agent consensus theory
Authors: Qiuhong Liu ; Weiming Fu ; Jiahu Qin ; Wei Xing Zheng ; Huijun Gao Abstract: This paper is concerned with developing a distributed k-means algorithm for the wireless sensor networks (WSN) where each node is equipped with sensors. The underlying topology of the WSN is supposed to be strongly connected. The consensus algorithm in multi-agent consensus theory is utilized to exchange the measurement information of the sensors in WSN. To obtain a faster convergence speed as well as a higher possibility of having the global optimum, a distributed k-means++ algorithm is firstly proposed to find the initial centroids before executing the distributed k-means algorithm. The proposed distributed k-means algorithm is capable of partitioning the data observed by the nodes into measure-dependent groups which have small in-group and large out-group distances. Simulation results show that the proposed distributed algorithms can achieve almost the same results as that achieved by the centralized clustering algorithms. 2017 Best conference paper award for IEEE ICIT 2016 This paper is presented at the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), check full paper at: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7475096 ...

